https://www.universetoday.com/147240/earth-observation-satellites-could-be-flown-much-lower-than-current-altitudes-and-do-better-science/#more-147240 LEO => 低軌道沒有公認的嚴格定義。一般高度在2000公里以下的近圓形軌道都可以稱之為低軌道
VLEO 極低地球軌道(VLEO)意指地球軌道高度低於250公里,因為它更接近地表,在這些軌道上運行的觀測衛星更具優勢。這些優勢使得在極低軌道上更簡單和更小的衛星足以與高軌道衛星的性能相匹配,且這更小的衛星,成本將更低。但是,隨著軌道高度的降低,空氣密度增加,作用於衛星的空氣阻力也會增加
VLEO orbits are usually defined as those below 450 km. The upper atmosphere at that altitude contains atomic oxygen. The atmospheric oxygen that we breathe is molecular oxygen (O2), meaning two oxygen atoms bound together. In the Earth’s upper atmosphere, the Sun’s ultraviolet light splits molecular oxygen into atomic oxygen. So atomic oxygen is unbound, meaning that it’s highly reactive. It’s just waiting to bond with something.

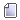
The volume fraction of the main constituents of the Earth’s atmosphere as a function of height according to the MSIS-E-90 atmospheric model. Atomic oxygen is shown in blue, and is most dense between 200 and 400 km. Image Credit: By Amaurea – Own work, CC0,
https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=71001656oxygen erosion 氧侵蝕