洪大哥:
想跟您請教一下
將彗星的色調調成最後一張圖
呈現不同的色層
有特別的科學意義嗎?
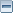
主要想強化並顯現彗髮左下(南南東)方的噴出物[請比對第二張圖]
作用與曹兄的灰階處理類似:
http://familystar.org.tw/index.php?option=com_smf&Itemid=45&topic=3967.15但灰階較難同時顯現噴出物與氫雲以至彗髮內部不同亮度與顏色的層次,假色則可!
{樓上上面第3圖可見假核,最後一張圖則未顯現,若先作了HDR合併再作假色則應同時可見?!}
彗星影像予以「假色處理」或「浮雕色階」處理,業餘或科普推廣上主要是想藉以凸顯彗星中的結構特徵,如暗淡的離子尾、細微的噴發物質或斷裂扭曲的纖維狀噴出團塊及離子態發光細絲。也可強化彗星假核的尺度變化、位置及聚集度(Condensity),還有如17P或H-B彗星彗髮內的像是一圈圈的漣漪一樣的Parabolic Hood也可清晰顯現出來。不過,Pro的正規觀測假色處理主要用來對應不同部位的不同組成或密度分佈:
例如:
http://www.lulin.ncu.edu.tw/DeepImapct.htmDeep Impact號撞擊9P/Tempel 1前所拍攝的影像經假色處理後 ,有助於比對撞擊前後彗星氣體和塵埃的變化
http://www.tam.gov.tw/cgi-bin/Message/MM_msg_control?mode=viewnews&ts=480ed088:7d11&theme=/3790000000/379040000E/379041700E/tam.message2&layout=波耶提尼彗星進行假色處理,以使彗髮結構更為明顯
http://starchild.gsfc.nasa.gov/docs/StarChild/questions/question20.htmlWhat is meant by "false color"?
The term "false color" is used to describe what astronomers (and others) often do to images to make them more comprehensible. Long ago, when radio astronomers first started generating images of sources, they wound up with essentially images that were just shades of gray - ranging from pure black to pure white. Each shade represented the intensity of the radio emission from a particular part of the object. Radio astronomers took their shades-of-gray images and converted them to color ones by assigning red to the most intense radio emission and blue to the least intense emission recorded on the image. Intermediate colors (orange, yellow, and green) were assigned to the intermediate levels of radio intensity. Black was assigned to places in the image in which there appeared to be no radio emission.
This process allows astronomers to more quickly recognize features in the images.
Typically, when looking at a photograph, the human eye can only distinguish about 16 shades of gray from one another. Using millions of colors, instead, we can often bring out details in an image that we might otherwise miss. These days, just about every area of astronomy creates "false color" images.